Poaceae. a Generalized (threeflowered) spikelet. b Flower (lemma... Download Scientific Diagram

Brew True Back To Basics Barley
FLORAL BIOLOGY OF BARLEY INTRODUCTION Kingdom: Plantae - Plants Subkingdom: Tracheobionta - Vascular plants Superdivision: Spermatophyta - Seed plants Division: Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants Class: Liliopsida - Monocotyledons Order: Cyperales Family: Poaceae - Grass family Genus: Hordeum - barley Chromosome number : 2n= 14 BARLEY
Plantae Hormonemediated inflorescence patterning in barley () Plantae
Barley ( Hordeum vulgare) is a plant of the Poaceae family. It is a cereal, like oats, rice, wheat or corn. Traditionally, barley fruits have been used to feed animals. Barley has been very important for agriculture and it still continues being so, just think that is the cereal that has a higher production after wheat, maize and rice.

Plant Minerals, Heavy Metal Detox, Barley Fulvic Barley
4 Barley Remains of nucellar epidermis Aleuron~ layer Fig. 1.3 A diagram of the microscopic details of the structures found at the ventral furrow. testa all over the grain except at the apex, where it may be in folds and carry the vestiges of the ovary tip. It may have a more open structure

Barley Free Stock Photo Closeup of barley growing in a field 11699
1. Structure of barley Source publication Chemical Composition in Barley Grains and Malt Quality Chapter Full-text available Jul 2010 Glen Patrick Fox Barley is used for a wide range of.

RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 25 Families of Angiosperms SabDekho
Summary This chapter focuses on the cultivated species of Hordeum vulgare L ., which includes both the six-rowed and two-rowed types. It discusses the morphology and anatomy according to the various plant parts: seed, roots, shoots, flower, and mature spike.

Barley Crop Improvement
Download scientific diagram | Isolated barley flower and its organs. (A). Barley flower.; (B). Lateral spikelets. (C). Caryopsis. (D). Stamens. (E). Lemma. (F). Palea. Scale-1 mm. from publication.

Edit free photo of Barley,spike,cereals,barley field,grain
5 Citations Abstract Barley, like other plants, is highly variable. Varieties differ greatly in their morphological and other characters, and a wide variation of characters occurs in 'pure races'. When a character is quantified for a group of plants this number is usually some sort of an average. A wide range of individual values will occur.
Foxtail Millet Plant Diagram
Barley (Hordeum vulgare), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods.

Cereals Education Cereals Kids Barley Plant, Rice Plant, Wheat Tattoo, Cereal Plant, Types Of
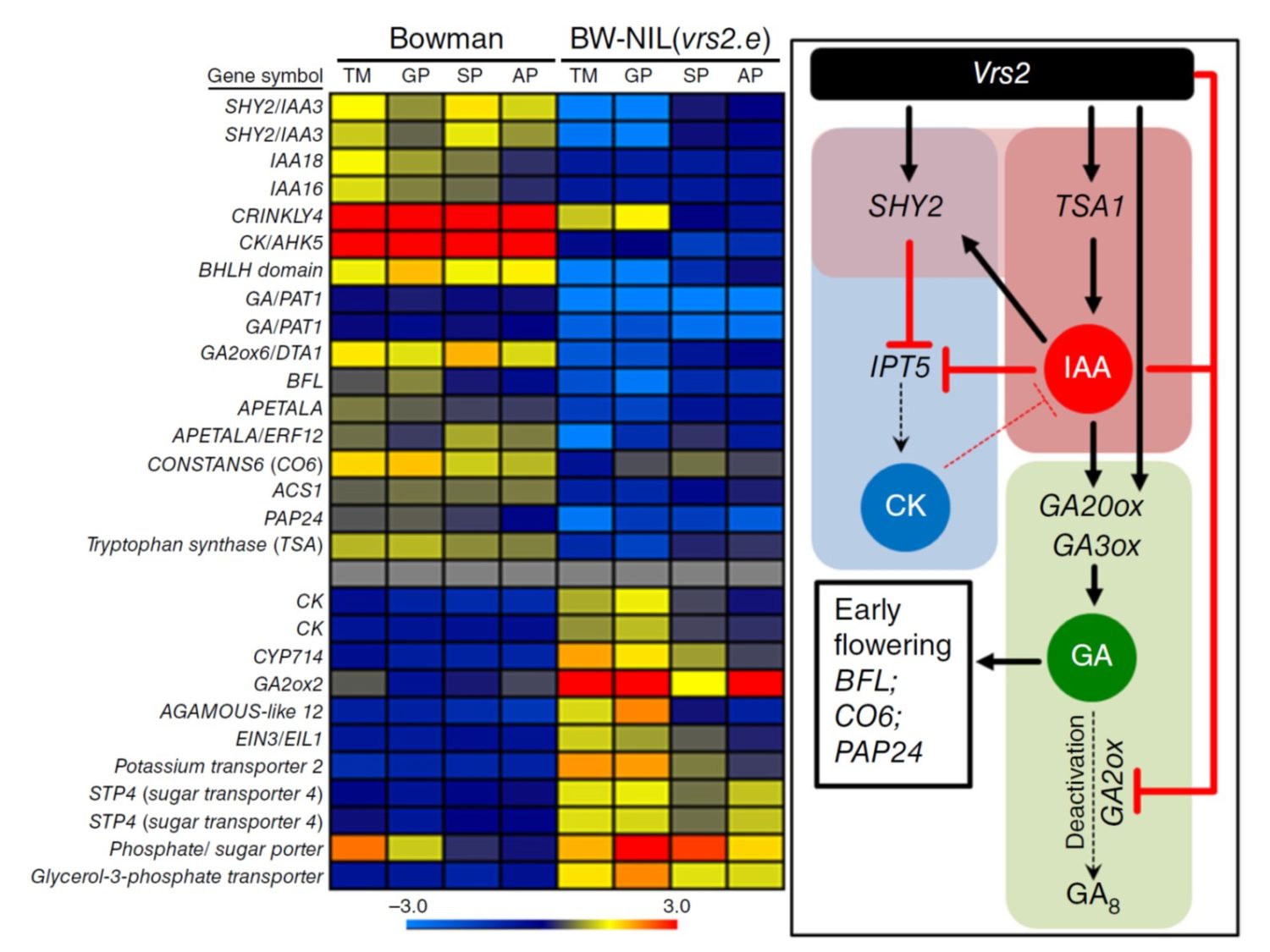
A new study finds that regulation of hormone levels during development is crucial for determining the arrangement of flowers on a barley inflorescence, opening new doors for increasing grain yield.

Inflorescence Spikelet
Barley possesses an indeterminate "spike"-type inflorescence that forms basic floral structures, called spikelets, in a distichous pattern along its central axis (termed rachis). Each rachis node.

Transcriptional landscapes of floral meristems in barley Science Advances
A spike inflorescence is formed by coordinated cell divisions of the inflorescence meristem (IM) that acropetally produces axillary meristems, each subtended by a leaf meristem forming so-called double ridges (DRs; Fig. 1A ). DR formation constitutes the first visible reproductive structures during early spike development.
Barley
THE grass leaf develops from a primordium, which grows out from the shoot apical meristem. At later stages of development, the primordium generates files of cells that either extend from the base to the tip of the leaf or produce stem internode tissues (Poethig 1984).The mature leaf consists of the sheath, the blade, and the border between these two domains, the so-called auricle-ligule.

Exploring the function of MADSbox genes in barley inflorescence development Faculty of
Barley has a diploid chromosome number of 14 and is self-pollinating. In 2016/2017 barley production worldwide was 145 million metric tons. This puts barley in fourth place in terms of production behind corn, wheat, and rice. The main barley producing countries are Russia, Germany, France, Ukraine, Australia, and Canada (Fig. 1). Barley is a.
Schematic diagram representing barley grown with or without competition... Download Scientific
floral development may not continue. Floral development in wheat and barley thus resembles a two-phase system, with the initiation of spikelet primordia on the apex, which is then fol-lowed by floral morphogenesis only if external and internal conditions are favourable (Aspinall, 1966). These earlier physiological studies of shoot apex develop-
.jpg?width=1200&name=Barley Leaf Diagram_900x600 (2).jpg)
2019 Protecting barley at T2
The flowers, group together in a central axis or rachis which is composed of nodes and internodes, which bears a group of three spikelets. Spikelets have only one flower. Each barley floret comprises of lemma, palea, lodicules, androecium and gynoecium in the model proposed by Forster et al. . As described in the section "types of barley.

Hulled barley milling process diagram and photographs, steps 7 to 10... Download Scientific
flowering and fruiting part of the plant. The floral organs of barley, as of other grasses, are different from those of ordinary flowering plants, though the essential sexual parts are the same. The unit of the inflorescence is the spikolot, which may contain only one flower, as in barley, or several, as in wheat.